Prehistoric music was used for entertainment, as well as other purposes like luring animals in, scaring them, and notifying the tribe members of the group’s location. However, this music was passed on orally from one generation to another.
However, the first written music piece was Hurrian Hymn No. 6, which was recorded about 4000 years ago, using the music notes. So, what are music notes? How were they invented?
Music notes refer to the sound, including the pitch and duration that make up music. So, music is composed of blocks of notes composed together. Keep on reading to learn more about music notes and what they mean.
What Are Music Notes?
In musical notation, music notes represent the pitch and duration of the sound.
By identifying the music notes, instrumentalists and other artists are able to comprehend, analyze, and perform the musical piece. Notes with similar frequencies are grouped under the same pitch class.
Music notes are named differently in various parts of the world.
In most European countries, Latin-American countries, Arabic-speaking, and Persian-speaking countries, music notes are named using the solfege naming convention. They’re called do-re-mi-fa-sol-la-si.
In English-speaking and Dutch-speaking countries, including Canada and the USA, notes are represented by the Latin letters A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. In Germany, the same naming technique is followed, but the letter H is used instead of the letter B.
In traditional Indian music, the musical notes are called svaras and are named after the notes Sa, Ra, Ga, Ma, Pa, Dha, and Ni.
In melodic music, notes refer to the vibrations that can be produced by conventional instruments like percussion instruments, woodwinds, brass, strings, vocals, and even less traditional instruments like car horns and banging cooking pots.
Combining music notes is a way of recording music and saving it. The notes are named based on the key where they represent. So, for example, C# is found in the A major scale, while the note Db is the same note found in the Bb minor scale.
How Are the Notes Named?

The first reference to the octave system was mentioned by Ptolemy, who called it the complete system because it contained all the variations of the octave. Other smaller-range note systems were considered to be incomplete.
In the 6th century, Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, a Roman philosopher, and consul, established a system that was later used to set the foundation of medieval music.
He used the first fourteen letters of the alphabet to refer to notes that made up the 2-octave range which was used in early music. The letter J wasn’t used because it was invented in the 16th century.
The Boethian notation used letters and numbers to refer to the octave range and frequency of notes and was set as follows: A 2 B2 C3 D3 E3 F3 G3 A3 B3 C4 D4 E4 F4 G4.
Later on, this system was extended to include 3 octaves, and the repetition of the letters A to G was introduced to indicate different octaves.
For the second octave, the letters were written in lowercase and they were repeated to indicate the presence of the third octave.
In Italian, Spanish, French, Albanian, Russian, Arabic, and Turkish music, the notes are named differently based on the first six musical phrases of a Gregorian chant called Ut queant laxis. These notes composed what we know as the solfège system.
The C major scale is the simplest example of a major scale and is obtained using natural tones or the white keys on the piano. As a result, this is usually the first scale taught in music schools because it doesn’t contain any black keys, unlike other scales.
What is the Octave?

The octave is the eighth note and is the same as the first one but double its frequency. Thus, the word octave also refers to the span between a note and another one which has double its frequency.
Also called the diapason, the perfect octave relationship is a natural phenomenon and refers to the interval between the first and second harmonics of the series in an octave.
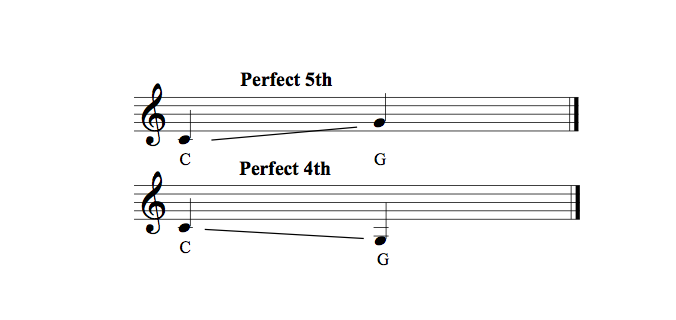
In Western music, notes of the same letter and pitch class are separated by an octave. The octave is one of the perfect intervals in music notation.
Others include the unison, which refers to two musical parts of the same pitch; the perfect fourth, which refers to four staff positions; and the perfect fifth, which refers to a pair of pitches in the ratio 3:2.
The notes are repeated in the same octave and appear in order. Then, these notes repeat themselves in the same pattern in a new octave.
The octave system combines a letter name with an Arabic numeral to signify the octave. There two most common systems to define notes and octaves, are the Helmholtz pitch notation and the scientific pitch notation. Other systems are less common.
Every note is defined by its sound and its position in the octave. For example, note A1 is the note A found in the first octave, while the C8 is the note C and is found in the eighth octave.
Accidentals modify the sounds of notes by raising or lowering a semitone or half-step of the note.
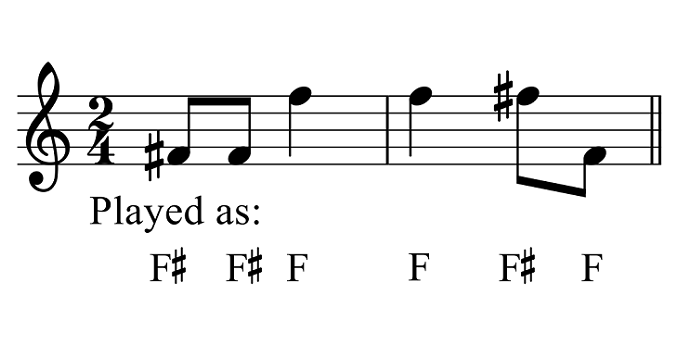
The sharp sign ♯ raises the music note by a half-step, and a flat ♭ lowers it by a half-step. The accidentals are written after the note, so B♯ represents B-sharp, while B♭ is B-flat. B natural or B is noted by B♮.
In some cases, the accidentals are noted by a suffix. For example, the suffix “is” refers to the sharp accidental, while the suffix “es” refers to the flat accidental.
This system is mainly used in non-English speaking countries and originated in Germany. The suffix “s” is used after the notes A and E.
There are 88 keys in the piano and 12 music notes, including seven whole notes and five flats, and equivalent sharps. The sharp and flat notes are named after the key signature used. For example, D sharp is the same E flat and refers to the same note.
What is a Note Frequency?
The note frequency is related to the physical component of the music or vibrations. Note frequencies are part of music theory, which analyzes the timing, structure, and pitch of the music to create different sounds.
A musical scale is composed of a set of pitches, and the most common type is the diatonic scale, which is made of five whole steps and two half steps in every octave.
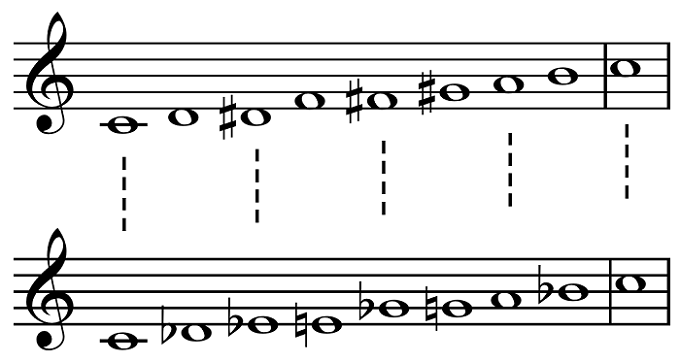
However, other scales were used in different eras and parts of the world. Each frequency is expressed in hertz or Hz.
The Divje Babe flute is made of a cave bear femur and follows the diatonic scale. Although there’s no documentation of how this flute was used or why it was made, it proves the existence of musical instruments about 43,000 years ago.
However, a part of the flue is missing. Nevertheless, the remaining holes indicate the presence of four notes. These four notes are spaced adequately like they would in a modern minor scale.
What Are the Most Harmonious Intervals?
The most harmonious music intervals are the perfect fourth and perfect fifth, around which most Western melodies are built. Although other intervals sound pleasing, any music with these intervals sounds more harmonious.
Other intervals can sound dissonant because they contain minor and major tones and semitones.
These dissonant intervals refer to two intervals that are placed next to each other and sound challenging to listen to. Musicians add these intervals to highlight the harmonious intervals.
By combining the notes of the harmonious and dissonant intervals, musicians are able to build tension and release, which is what makes music catchy and interesting.
A music composition that is entirely made of harmonious intervals sounds pleasing but can be boring or lifeless. At the same time, too many dissonant intervals can make the music disturbing and difficult to understand.
Beethoven and Mozart are both known for including dissonant intervals in their musical compositions to add an element of excitement and surprise that makes the melodies irresistible.
String Quartet No. 19 by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart is known for the alternating between minor and major chords that make this string quartet nicknamed dissonance.
In modern music, the theme song of the movie Jaws, which is composed by John Williams, is another clear example of using unexpected minor chords to create suspense and tension.
In that sense, creating pleasant and appealing music is mainly dependent on using harmonious intervals while adding one or two dissonant intervals to add a little spice or tension.
Why is Middle C So Important?
The middle C or C4 is not located in the absolute middle of the piano, but it’s near the middle.
The treble clef and bass clef have ten lines, and the space between them can be considered the 11th line, which is between the two, where the middle C or C4 is located.
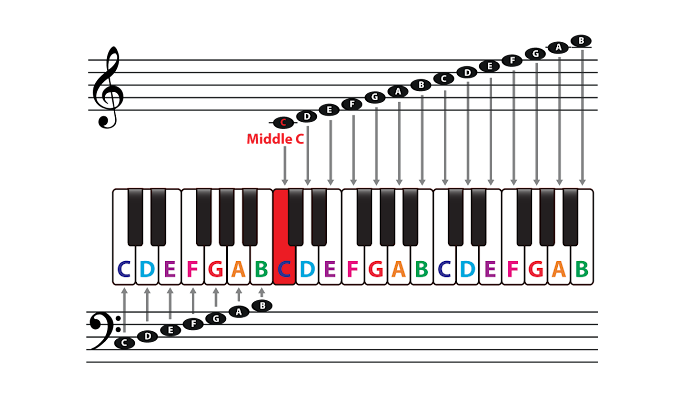
While playing music, the C4 acts as a guide as it helps players position their hands on the piano’s keyboard.
The C4 acts as a distinctive border between the notes played using the left hand, and the notes played using the right hand. Lots of Western music and piano songs start with C4.
Locating the middle C is a little different on an electric keyboard because it doesn’t have 88 keys. The player should start from the left and count the keys to locate the middle C position, depending on the keyboard size.
- If the keyboard has 88 keys, the middle C is C4.
- If the keyboard has 76 keys, the middle C is C3.
- If the keyboard has 61 keys, the middle C is C3.
- If the keyboard has 49 keys, the middle C is C3.
What is a Note Value?
The note value refers to the duration of the note. It’s determined by the shape or texture of the notehead and the presence or absence of the stem. Other factors include the flags or tails. A rest refers to a period of silence of equivalent duration.

Note values are indicated as follows.
- A larga or maxima is a long note with a value of 8. It was widely used in the music of the 13th and 14th centuries. It looks like a rectangle with the stem usually facing down.
- A long or longa note has a value of 4. First, it had a filled notehead, and then it was written using an empty one.
- A whole double note has a value of 2. It’s also called a breve and lasts two times longer than a whole note.
It’s the second-longest note in modern music. The word breve is derived from the word “brief” as this note was considered short compared to other notes used in early music.
- A whole note or semibreve has a value of 1. It lasts as two half notes or four quarter notes. It has a hollow note head with no stem. A whole rest is written as a filled-in rectangle.
- A half note has a value of 1/2. This note was called minima in medieval music because it was the shortest of the five note values used in early music notation.
It has an oval hollow head and a stem with no flags. The line is drawn to the right of the note and facing up if it’s below the middle line of the staff. It’s drawn to the left of the notehead and facing down if it’s above the middle line of the staff.
- A quarter note or crotchet has a value of 1/4and is played for one quarter for the value of a whole note.
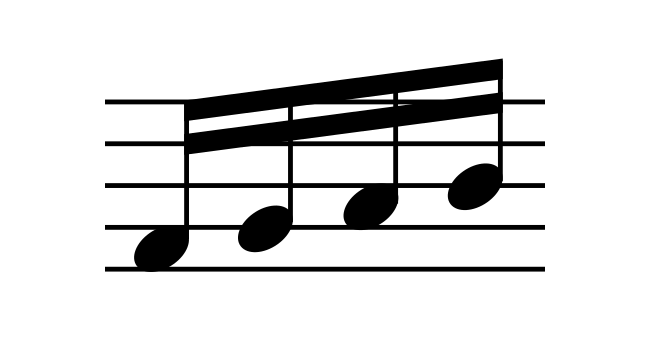
It’s represented by a filled-in oval head and a straight stem without flags. The direction of the head and stem depends on the position of the note with respect to the lines.
- An eighth note or quaver has a value of 1/8 of a whole note. It’s featured with a filled-in oval head with a stem and a flag.
- A sixteenth note or a semiquaver has a value of 1/16 or half the value of a 1/8 note. It’s represented with a filled-in oval head and a stem with two flags. A sixteenth rest denotes silence of the same duration.
- A thirty-second note or a demisemiquaver note has a value of 1/32 of a whole note. It’s represented by a filled-in oval head with a stem and three flags or beams that slightly curve.
The flags are on the right side or left side of the stem, depending on the position of the note.
There are shorter notes like sixty-fourth note, hundred twenty-eighth note, and two hundred and fifty-sixth note. These faster notes are prominent in different music pieces like Mozart’s Je Suis Lindor.
What Are Modifiers?
Modifiers are signs that are added to modify the value of a note. The modifier is a dot that adds value to the note value making it one and a half times longer than its original duration.
When two dots are added, they will add two lower note values, so the note will be one and three quarters its original duration.

When a note is divided into values other than two, a tuplet is used. This is called an irrational rhythm, artificial division, or gruppetto.
The most common type of a tuplet is a triplet which divides the note’s value into three equal parts.
For example, two-quarter notes have the same value as a single half note, and three triplet quarter notes have the same value.
A modifier is indicated by a number drawn over the beam that connects the notes together. For example, if the notes have the number 7 written above the beam, this refers to the same duration that would typically be occupied by four notes.
What Are the Notation Systems?
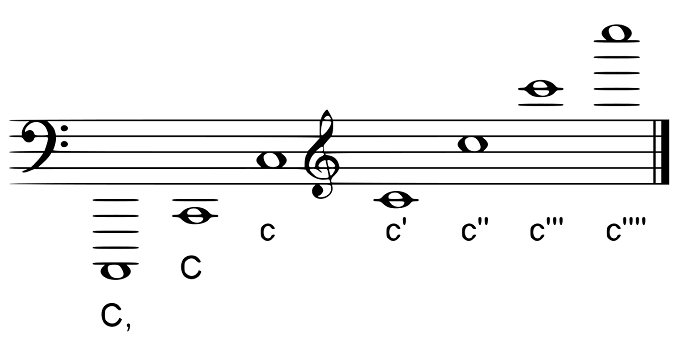
The two most common notation systems are the Helmholtz pitch notation system and the scientific pitch notation system. Both systems have some similarities as they both start from a C rather than an A.
The Helmholtz pitch notation system was invented by Hermann von Helmholtz and included upper and lower case letters from A to G with prime symbols. It accurately defines pitches in classical music.
The other system is the scientific pitch notation or the SPN. It refers to the musical pitch by combining note names with accidentals and a number to refer to the octave. In most cases, this notation system is used to determine the range of an instrument.
What Are the Other Types of Music Notes?
In addition to regular notes, there are other music notes that are used in musical notations.
- A ghost note has a rhythmic value but no pitch and is indicated with the letter X instead of the oval head that is otherwise used to display a note. A ghost note is also called a silenced or dead note.
- A grace note refers to a musical ornament printed smaller than a regular note to indicate that it’s not essential.
- A shape note is added to music notes to facilitate singing. It’s also called a character note and is usually used to help singers learn the vocals of a song faster and better.







